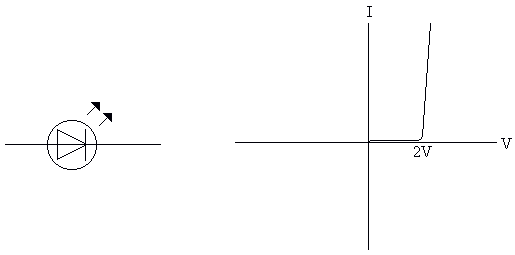A diode only allows current to flow one way. Below is the current-voltage characteristics of different diodes. Here are some of the terms you may see:
Peak Inverse Voltage (PIV) = Maximum reverse voltage allowed.
Forward current rating = maximum forward current allowed.
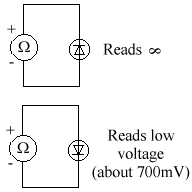
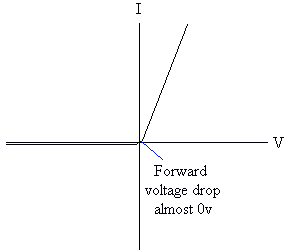
There is a forward turn on voltage - The silicon diode will only allow current through it if there is 0.7V flowing through it (i.e. it requires 0.7V to turn itself on). Note that it takes 0.7V out of the supply, so if you have a supply voltage of 6V, & a diode correctly inserted in the circuit, the voltage after the diode will only be 5.3V, because it has taken 0.7V.
Note also that the diode has a peak inverse voltage - There is normally no current flowing through a diode in reverse.
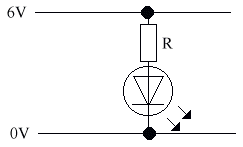
The Light Emitting Diode (LED)
The Light Emitting Diode (LED) is made of a different material. Its forward voltage drop is 2v, & the maximum current is about 50 mA. It requires a series resistance to limit the current. The LED is generally used as an indicator, as it doesn't give off enough light to be used as a light source.
For example, to run an LED from a 6V battery at 5mA:
R = V / I = (6-2) / 5 = 0K8 = 800R
- To turn an alternating current (AC) to a direct current (DC).
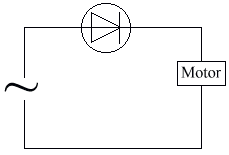
- To protect against incorrect polarity.
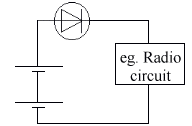
- To limit the voltage.
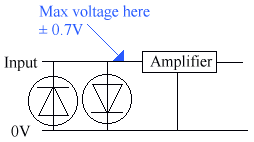
To test a diode, we use an ohmmeter.